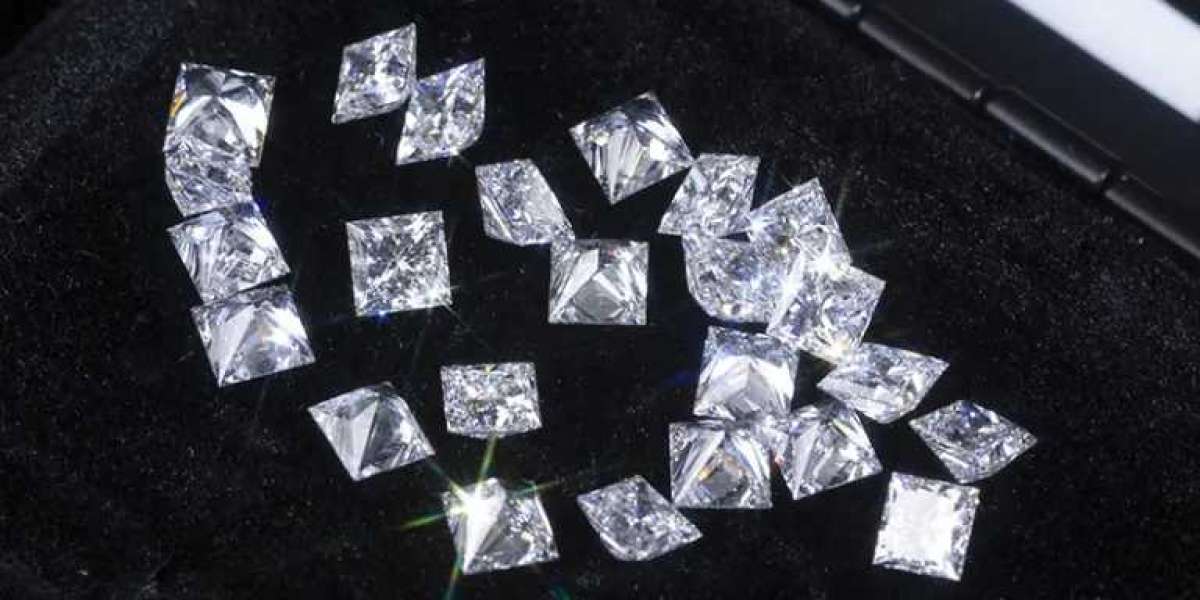
For centuries, diamonds have been a symbol of luxury, elegance, and romance. However, with the advent of lab-grown diamonds, the traditional diamond industry has been disrupted, leaving consumers with a dilemma: natural or lab-grown? While both types of diamonds have their own unique characteristics, understanding the differences between them is crucial in making an informed decision. In this article, we will delve into the world of diamonds, exploring the differences between natural and lab-grown diamonds.
The Origin of Natural Diamonds
Natural diamonds are formed deep within the Earth's crust, over millions of years, through a process of high pressure and temperature. These lab diamond manufacturers are mined from the Earth's surface, often using large-scale excavation and drilling techniques. The rarity and uniqueness of natural diamonds are due to the complex geological processes that create them. Natural diamonds have inclusions, imperfections, and characteristics that are a result of their natural formation process. These imperfections, such as feathers, inclusions, and blemishes, are often considered to be a natural diamond's fingerprint, making each one unique.
The Science Behind Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds, also known as cultured diamonds or synthetic diamonds, are created through a process of high-pressure high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes replicate the natural processes that create diamonds, but in a controlled laboratory environment. Lab-grown diamonds have the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as natural diamonds, but with fewer inclusions and imperfections. The CVD process involves the deposition of carbon atoms onto a substrate, while the HPHT process involves subjecting a diamond "seed" to extremely high pressure and temperature. Both processes result in diamonds that are chemically, optically, and physically identical to natural diamonds.
The Differences in Characteristics
One of the most significant differences between natural and lab-grown diamonds is their characteristics. Natural diamonds have inclusions, imperfections, and blemishes that are a result of their natural formation process. Lab-grown diamonds, on the other hand, have fewer inclusions and imperfections, making them appear more uniform and flawless. Additionally, lab-grown diamonds often have a more consistent color and clarity, whereas natural diamonds can have a range of colors and clarity levels. The cut, polish, and symmetry of lab-grown diamonds are also often more precise, due to the controlled laboratory environment.
The Environmental and Social Impact
The environmental and social impact of natural diamond mining has been a topic of concern for many years. Traditional diamond mining often involves large-scale excavation, deforestation, and water pollution, resulting in significant environmental damage. Additionally, the diamond industry has been linked to human rights abuses, such as child labor and conflict diamonds. Lab-grown diamonds, on the other hand, have a significantly lower environmental impact, as they require minimal resources and energy to produce. Lab-grown diamonds also eliminate the risk of conflict diamonds and human rights abuses.
The Price Difference
One of the most significant advantages of lab-"../">grown diamonds is their price. Lab-grown diamonds are often 20-40% less expensive than natural diamonds, making them a more affordable option for consumers. The lower price point is due to the reduced production costs, as lab-grown diamonds do not require the same level of excavation, mining, and processing as natural diamonds.

The Certification and Disclosure
As the lab-grown diamond industry continues to grow, certification and disclosure have become increasingly important. Reputable gemological laboratories, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the International Gemological Institute (IGI), provide certification and grading reports for both natural and lab-grown diamonds. These reports disclose the diamond's origin, characteristics, and any treatments or enhancements. It is essential for consumers to request certification and disclosure when purchasing a diamond, to ensure that they are aware of the diamond's origin and characteristics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between natural and lab-grown diamonds is crucial in making an informed decision. While natural diamonds have their own unique characteristics and history, lab-grown diamonds offer a more affordable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly option. As the lab-grown diamond industry continues to evolve, it is essential for consumers to be aware of the differences and similarities between these two types of diamonds. By doing so, consumers can make a decision that aligns with their values, budget, and preferences.