Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is estimated that over 400 million people worldwide are living with this condition. Genital herpes can cause discomfort, emotional distress, and stigma for those affected. In this article, we will delve into the topic of genital herpes, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, and the possibility of a cure.
Understanding Genital Herpes:
What is genital herpes?
Genital herpes Cure is a viral infection primarily transmitted through sexual contact. It is caused by two types of the herpes simplex virus: HSV-1 and HSV-2. While HSV-1 is commonly associated with oral herpes (cold sores), HSV-2 is typically responsible for genital herpes. However, it's important to note that either type can infect the oral or genital area.
Causes of genital herpes:
Genital herpes is most commonly transmitted through sexual intercourse, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. The virus can be passed on even if the infected person doesn't have any visible sores or symptoms. Sharing sex toys, engaging in close intimate contact, or having multiple sexual partners can increase the risk of transmission.
Symptoms of genital herpes:
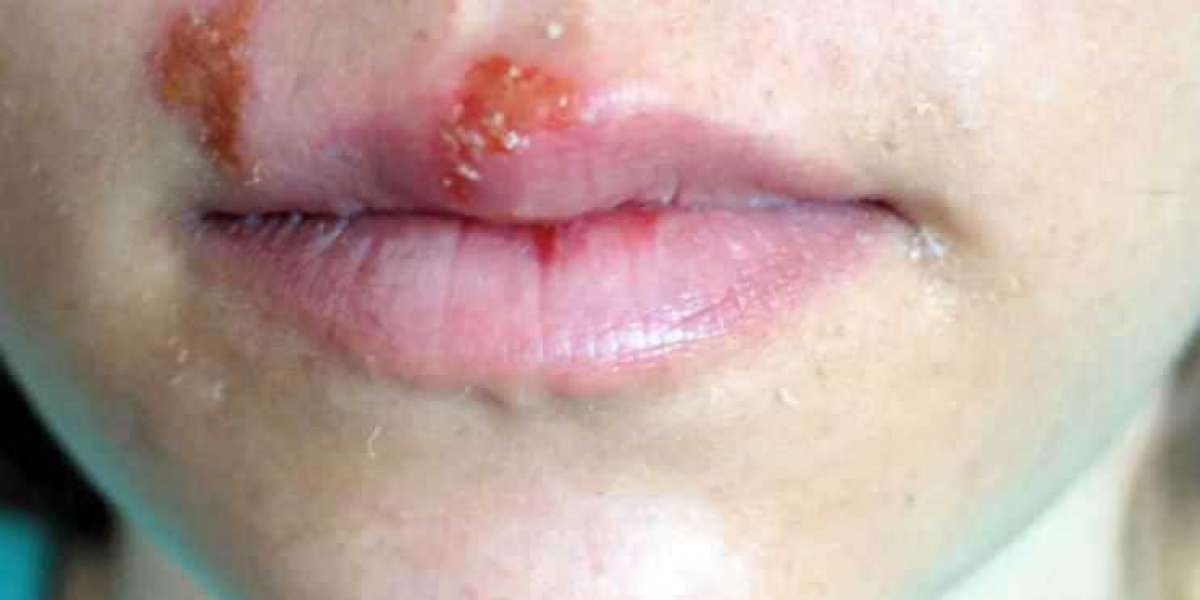
The symptoms of genital herpes can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience severe symptoms, while others may have mild or no symptoms at all. Common signs and symptoms include:
Painful, blister-like sores or ulcers in the genital or anal area
Itching or tingling sensations before the appearance of sores
Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
Flu-like symptoms, such as fever and body aches
Pain or discomfort during urination
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis of genital herpes:
To diagnose genital herpes, healthcare providers may perform a physical examination and collect a sample from the sore or lesion for laboratory testing. They may also conduct a blood test to detect the presence of herpes antibodies. It's important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Conventional treatment options:
While there is no cure for genital herpes, antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. These medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, work by suppressing the replication of the herpes virus. They can be taken episodically during outbreaks or as a daily suppressive therapy for individuals with frequent recurrences.
Prevention and Management:
Preventing the spread of genital herpes:
While genital herpes Cure is a lifelong condition, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of transmission to your partner or others. These preventive measures include:
Safe sex practices: Consistently using latex or polyurethane condoms during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of transmitting the virus. However, it's important to note that condoms may not provide complete protection, as the virus can be present in areas not covered by the condom.
Avoiding sexual activity during outbreaks: Refraining from sexual contact when active sores or symptoms are present can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Open communication: Discussing your herpes status with your sexual partner(s) is essential for informed decision-making and taking necessary precautions to prevent transmission.
Lifestyle changes for managing genital herpes:
Living with genital herpes may require making certain lifestyle adjustments to minimize outbreaks and manage symptoms. These include:
Maintaining a healthy immune system: Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress levels, and getting enough sleep can help support a strong immune system, which may reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that may exacerbate outbreaks, such as prolonged exposure to sunlight, excessive stress, or certain foods, can help manage the condition effectively.
Practicing good hygiene: Keeping the affected area clean and dry can help prevent secondary infections and promote faster healing of sores.
Conclusion:
Genital herpes Cure is a common and manageable condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. While a complete cure is yet to be discovered, there are various treatment options available to manage symptoms, reduce outbreaks, and prevent transmission. Additionally, ongoing medical research and advancements offer hope for potential cures in the future. By adopting healthy lifestyle practices, seeking emotional support, and staying informed, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing genital herpes.